Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are two usual illnesses that are prevalent amongst ladies. Although they are both familiar to anyone who has used marijuana, they are unique and unlike in effects, they are not the same. Let me explain what these conditions are, their signs, and causes, also how they can be taken care of.
What is PCOD?
PCOD, or Polycystic Ovary Disorder, happens when a woman’s ovaries produce a large number of immature or partially mature eggs. These eggs can develop into cysts. PCOD can cause:
- Irregular periods
- Weight gain
- Acne and other skin problems
- Hair loss
- Fertility issues
What is PCOS?
PCOS, or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, is a more serious condition where the ovaries have many small cysts. It affects a woman’s hormone levels and overall health. Symptoms of PCOS include:
- Irregular or no periods
- Excessive hair growth on the face and body
- Severe acne
- Weight gain, especially around the belly
- Thinning hair or hair loss
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Dark patches of skin, especially around the neck and armpits
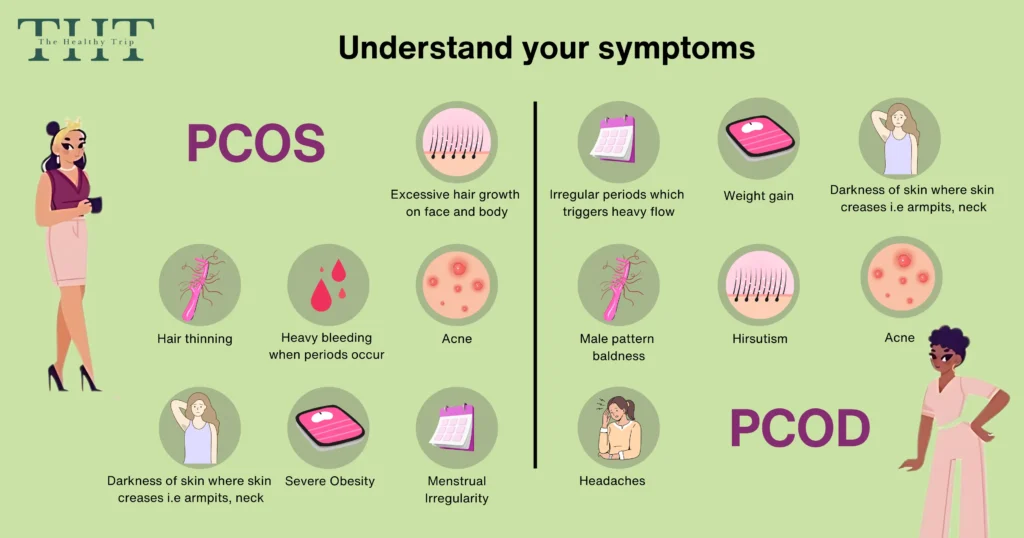
Difference Between PCOD and PCOS
While both PCOD and PCOS involve cysts in the ovaries, they have key differences:
- Severity: PCOS is generally more severe than PCOD.
- Hormonal Impact: PCOS has a more significant impact on the body’s hormones.
- Health Risks: PCOS is associated with higher risks of conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and infertility.
- Prevalence: PCOD is more common and less severe than PCOS.
Causes of PCOD and PCOS
While both PCOD and PCOS involve cysts in the ovaries, they have key differences:
- Genetics: A family history of PCOD or PCOS increases the risk.
- Hormonal Imbalance: High levels of male hormones (androgens) can disrupt ovulation.
- Insulin Resistance: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, which can lead to high insulin levels and weight gain.
- Inflammation: Low-grade inflammation is often found in women with PCOS and may contribute to the condition.
Diagnosing PCOD and PCOS
To diagnose these conditions, doctors will look at your medical history, do a physical exam, and may order blood tests and an ultrasound. They look for:
- Irregular periods
- High levels of male hormones
- Ovarian cysts seen on an ultrasound
Treatment Options for PCOD and PCOS
There is no cure for PCOD or PCOS, but treatments can help manage the symptoms:
- Lifestyle Changes: Eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly can help manage weight and symptoms. A diet low in sugar can be especially helpful.
- Medications: Birth control pills can help regulate periods and reduce male hormone levels. Metformin is often used for insulin resistance.
- Fertility Treatments: For women who want to get pregnant, fertility drugs or procedures like in vitro fertilization (IVF) might be needed.
- Surgery: In some cases, a surgery called laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD) can help restore normal ovulation.
Natural Ways to Manage PCOD and PCOS
In addition to medical treatments, some natural methods can help manage symptoms:
- Herbal Supplements: Supplements like inositol, cinnamon, and spearmint tea might help.
- Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can reduce stress and improve overall health.
- Regular Check-ups: Seeing your doctor regularly helps monitor symptoms and adjust treatments as needed.
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between PCOD and PCOS is important for managing these conditions. With the right lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and natural remedies, women with PCOD or PCOS can live healthy, fulfilling lives. If you think you might have PCOD or PCOS, talk to your doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.










